Myasthenia Gravis: A Comprehensive Overview of Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Introduction
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the muscles, leading to weakness and fatigue. This article provides a detailed overview of MG, including its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with MG or you’re simply interested in learning more about this condition, keep reading to gain valuable insights and knowledge.
1. Understanding Myasthenia Gravis
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia Gravis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the acetylcholine receptors in the muscles, impairing their ability to receive signals from the nerves.
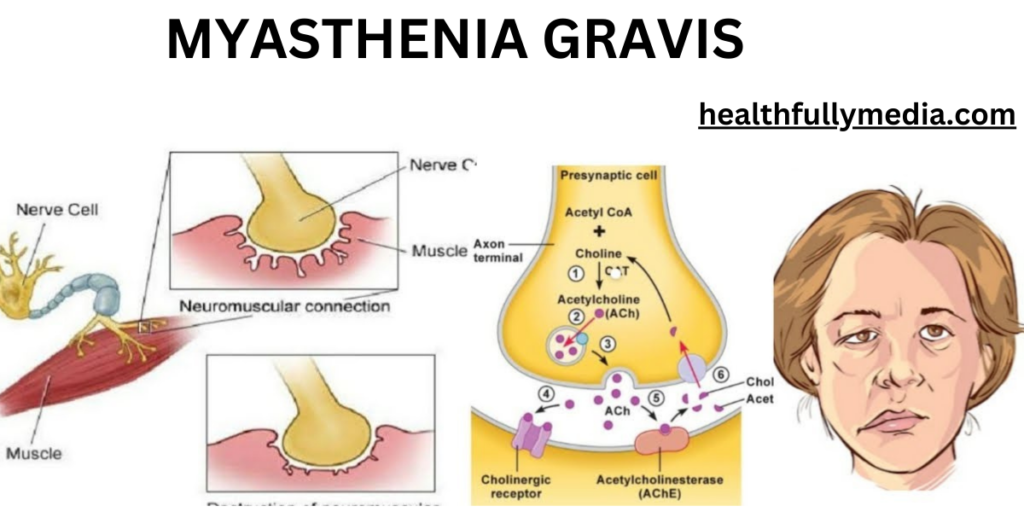
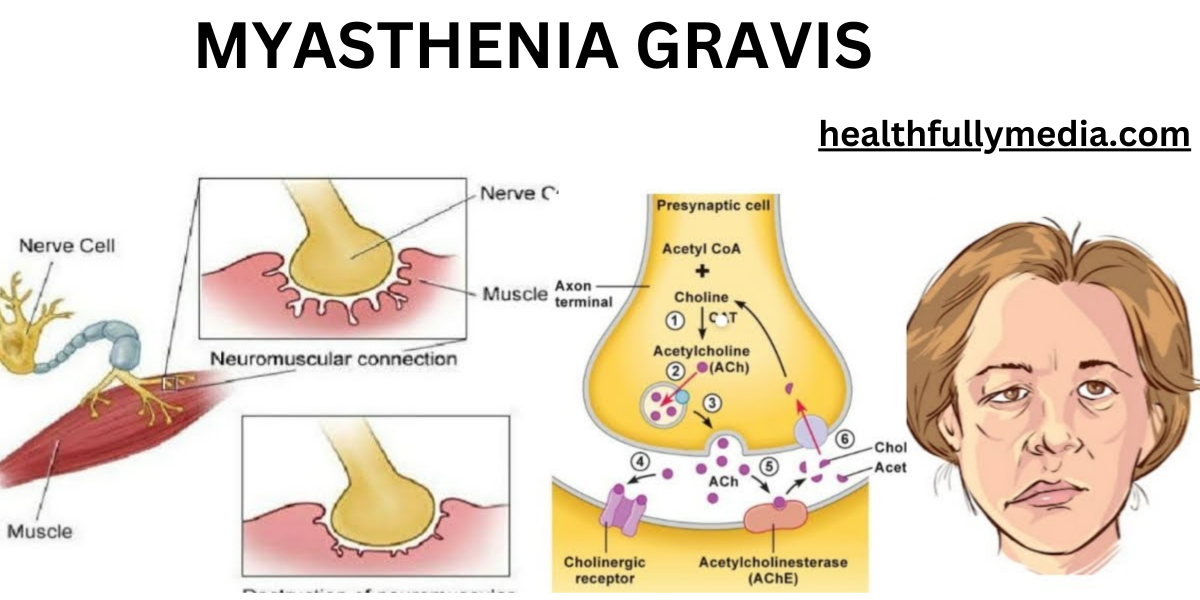
How does MG affect the body?
In a healthy individual, acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, attaches to receptors on the muscles, triggering muscle contractions. In MG, the immune system produces antibodies that block or destroy these receptors, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue.
2. Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
Muscle weakness and fatigue
The hallmark symptom of MG is muscle weakness, which typically worsens with activity and improves with rest. It commonly affects the muscles of the eyes, face, throat, and limbs, leading to drooping eyelids, difficulty chewing and swallowing, slurred speech, and weakened limb movements.
Difficulty with facial expressions and eye movements
People with MG often experience difficulty in making facial expressions, such as smiling or frowning. They may also have trouble controlling their eye movements, resulting in double vision or eyelid drooping.
Impaired speech and swallowing
MG can affect the muscles involved in speech and swallowing, causing speech to become slurred or nasal-sounding. Swallowing difficulties may lead to choking or aspiration of food or liquids.
3. Causes and Risk Factors
Autoimmune dysfunction
The exact cause of MG is unknown, but it is believed to involve an autoimmune response, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. In MG, the antibodies attack the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
The role of thymus gland
The thymus gland, located in the chest, plays a crucial role in the development of MG. In some cases, it is found that the thymus gland is abnormally large or contains tumors, which can trigger or worsen MG symptoms.
Genetic predisposition
Although MG is not directly inherited, certain genetic factors can increase the risk of developing the condition. Individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases are more likely to develop MG.
4. Diagnosis of Myasthenia Gravis
To diagnose MG, healthcare professionals employ several methods:
Physical examination and medical history
A comprehensive physical examination, including an evaluation of muscle strength and coordination, is performed to identify specific weakness patterns associated with MG. The doctor will also inquire about the patient’s medical history and any symptoms experienced.
Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies
EMG and nerve conduction studies help assess the electrical activity and functioning of the muscles and nerves. These tests can detect abnormalities associated with MG, such as a decrease in muscle response after repeated nerve stimulation.
Blood tests for specific antibodies
Blood tests are conducted to detect the presence of antibodies that target the acetylcholine receptors or other proteins involved in the neuromuscular junction. The presence of these antibodies helps confirm the diagnosis of MG.
5. Treatment Options
Medications for symptom management
Several medications are available to manage MG symptoms by improving neuromuscular transmission and reducing the activity of the immune system. These may include acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and monoclonal antibodies.
Thymectomy for certain cases
In individuals with MG and an enlarged thymus gland or thymoma, thymectomy (surgical removal of the thymus) may be recommended. This procedure aims to improve symptoms and reduce the production of abnormal antibodies.
Plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Plasmapheresis involves removing the antibodies from the blood plasma, while IVIG provides healthy antibodies to counteract the effects of the abnormal ones. These therapies are used in severe cases or as temporary measures to manage acute exacerbations.
6. Coping Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
Rest and conserving energy
Fatigue is a common symptom of MG, and it is essential to prioritize rest and conserve energy. Adequate sleep, regular breaks, and strategic planning of activities can help manage fatigue and minimize symptom flare-ups.
Physical therapy and exercise
Physical therapy exercises can improve muscle strength, coordination, and overall physical function. A physical therapist can design an individualized exercise program that focuses on specific muscle groups affected by MG.
Emotional and psychological support
Living with a chronic condition like MG can be challenging. Seeking emotional and psychological support from friends, family, support groups, or mental health professionals can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of the disease.
7. FAQs
1. What age group is commonly affected by Myasthenia Gravis?
MG can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects women under 40 and men over 60. However, it can occur in people of all ages, including children.
2. Can Myasthenia Gravis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for MG, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. With proper care, most individuals with MG can lead fulfillinglives.
3. Are there any natural remedies for managing MG symptoms?
While there are no natural remedies that can cure MG, certain lifestyle modifications may help manage symptoms. These include maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise within individual limits, and reducing stress levels.
4. Is pregnancy safe for women with Myasthenia Gravis?
Pregnancy in women with MG requires careful management and close monitoring by a healthcare team. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals to discuss the potential risks and benefits of pregnancy in the context of MG.
5. Can stress worsen the symptoms of MG?
Stress and fatigue can exacerbate MG symptoms in some individuals. Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques, stress-reducing activities, and adequate rest can help minimize symptom flare-ups.
8. Conclusion
Myasthenia Gravis is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. While there is no cure for MG, proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve quality of life for individuals living with this condition. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options, individuals with MG and their loved ones can navigate this challenging condition more effectively.
FAQs
- Q: What age group is commonly affected by Myasthenia Gravis? A: Myasthenia Gravis can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects women under 40 and men over 60. However, it can occur in people of all ages, including children.
- Q: Can Myasthenia Gravis be cured? A: Currently, there is no cure for MG, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. With proper care, most individuals with MG can lead fulfilling lives.
- Q: Are there any natural remedies for managing MG symptoms? A: While there are no natural remedies that can cure MG, certain lifestyle modifications may help manage symptoms. These include maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise within individual limits, and reducing stress levels.
- Q: Is pregnancy safe for women with Myasthenia Gravis? A: Pregnancy in women with MG requires careful management and close monitoring by a healthcare team. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals to discuss the potential risks and benefits of pregnancy in the context of MG.
- Q: Can stress worsen the symptoms of MG? A: Stress and fatigue can exacerbate MG symptoms in some individuals. Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques, stress-reducing activities, and adequate rest can help minimize symptom flare-ups