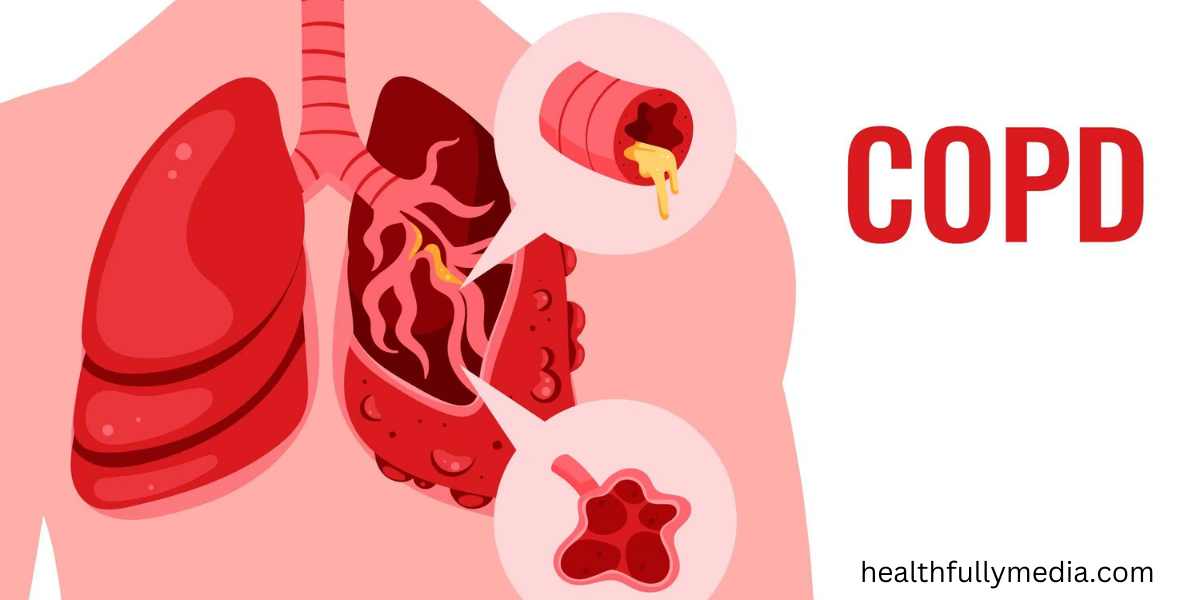
Introduction
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, posing a significant burden on individuals and healthcare systems. Recognizing the symptoms of COPD is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. In this article, we will delve into the various symptoms associated with COPD, their impact on daily life, and the importance of seeking appropriate treatment. Let’s explore the signs of COPD and discover how individuals can improve their quality of life.
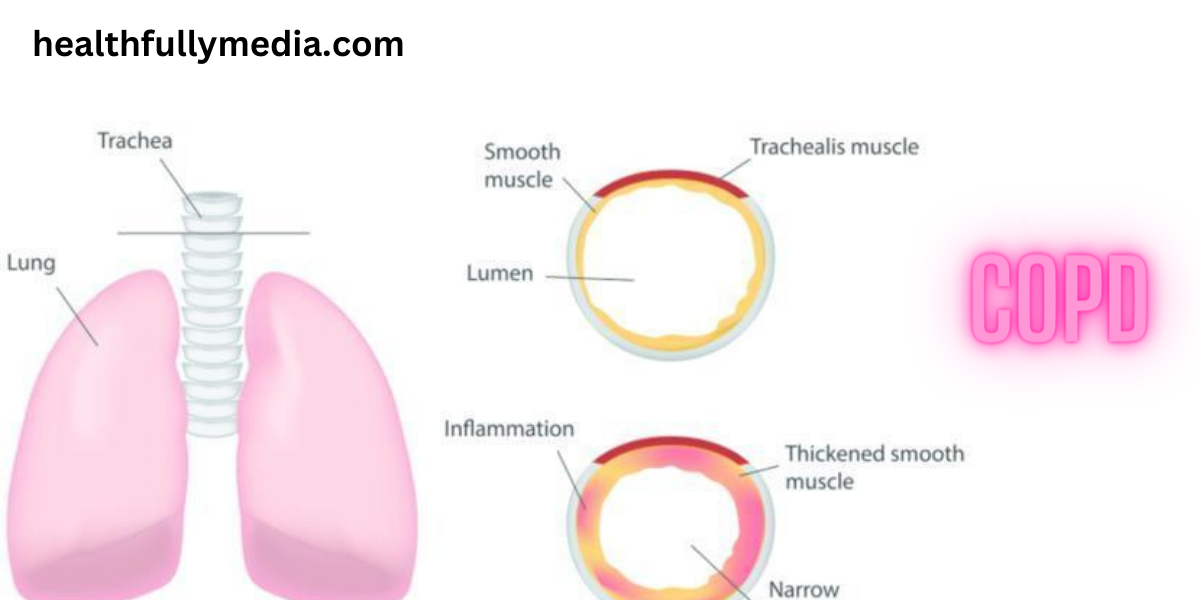
1. What is COPD?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung condition characterized by airflow limitation. It primarily includes two major conditions: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. COPD is usually caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards.
2. Persistent Cough and Sputum Production
A persistent cough accompanied by the production of excess mucus is one of the hallmark symptoms of COPD. This cough is usually worse in the morning and is often disregarded as a smoker’s cough. However, if it persists for three months or longer for two consecutive years, it may indicate chronic bronchitis, which is a common form of COPD.
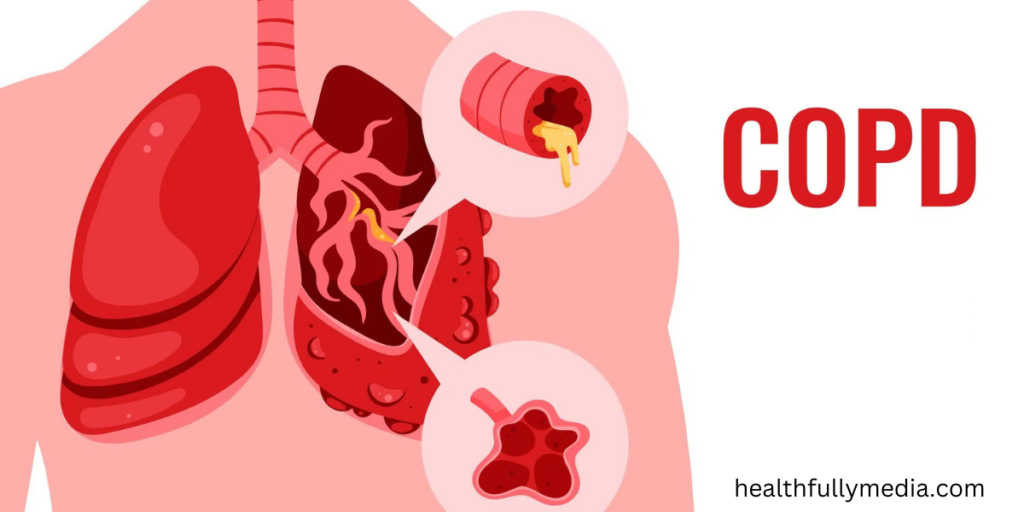
3. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is another prevalent symptom of COPD. Individuals with COPD often experience breathlessness during physical exertion or even while performing simple tasks. As the disease progresses, breathlessness can occur during rest as well, severely impacting the quality of life.
4. Wheezing and Chest Tightness
Wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing, and chest tightness are commonly observed in COPD patients. These symptoms arise due to narrowed airways and inflammation in the lungs. Wheezing and chest tightness can cause discomfort and make it challenging to breathe properly.
5. Fatigue and Reduced Energy Levels
COPD can lead to significant fatigue and decreased energy levels. The inefficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs results in reduced oxygen supply to the body, affecting overall energy levels. Fatigue can impact daily activities, leading to a decreased quality of life.
6. Recurring Respiratory Infections
Individuals with COPD are more susceptible to respiratory infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis. The damaged airways and compromised immune system make them more vulnerable to these infections. Recurrent respiratory infections can further exacerbate COPD symptoms and increase the risk of disease progression.
7. Unintended Weight Loss
Unintended weight loss is often observed in COPD patients. This can occur due to several factors, including increased energy expenditure while breathing, decreased appetite, and the body’s increased effort to fight the underlying inflammation. Weight loss can have a significant impact on overall health and worsen COPD symptoms.
8. Depression and Anxiety
COPD not only affects physical health but also takes a toll on mental well-being. The chronic nature of the disease, coupled with the limitations it imposes on daily activities, can lead to depression and anxiety. It is essential for COPD patients to receive emotional support and seek proper mental health care.
9. Seeking Proper Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing COPD effectively. If you or a loved one experience any of the aforementioned symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Treatment options may include medications, pulmonary rehabilitation, lifestyle modifications, and oxygen therapy, depending on the severity of the condition.

10. Conclusion
In conclusion, COPD is a progressive lung disease that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms associated with COPD is essential for timely diagnosis and proper management. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, fatigue, or other related symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. With proper treatment and support, individuals with COPD can lead fulfilling lives and improve their overall well-being.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Q: Can COPD be cured?
- A: While there is no cure for COPD, proper management can help control symptoms and slow down disease progression.
- Q: What are the risk factors for developing COPD?
- A: The primary risk factors for COPD include smoking, long-term exposure to lung irritants, genetic factors, and respiratory infections.
- Q: Can COPD be prevented?
- A: Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to lung irritants can significantly reduce the risk of developing COPD.
- Q: Is COPD only seen in elderly individuals?
- A: While COPD is more common in older adults, it can affect individuals of any age, especially those with a history of smoking or exposure to lung irritants.
- Q: How can pulmonary rehabilitation benefit COPD patients?
- A: Pulmonary rehabilitation programs help improve lung function, increase exercise capacity, and provide education and support for managing COPD symptoms