The Liver: An Overview
The liver, the body’s largest internal organ, plays a vital role in digestion, metabolism, detoxification, and the storage of nutrients. It is a complex organ with various blood vessels ensuring its proper function.
What is the Hepatic Artery?
The hepatic artery is a crucial blood vessel that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the liver. It branches off from the celiac artery, which arises from the abdominal aorta. This oxygenated blood is essential for the liver’s metabolic activities and overall health.
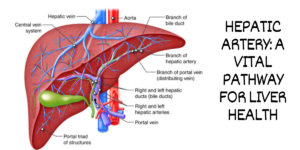
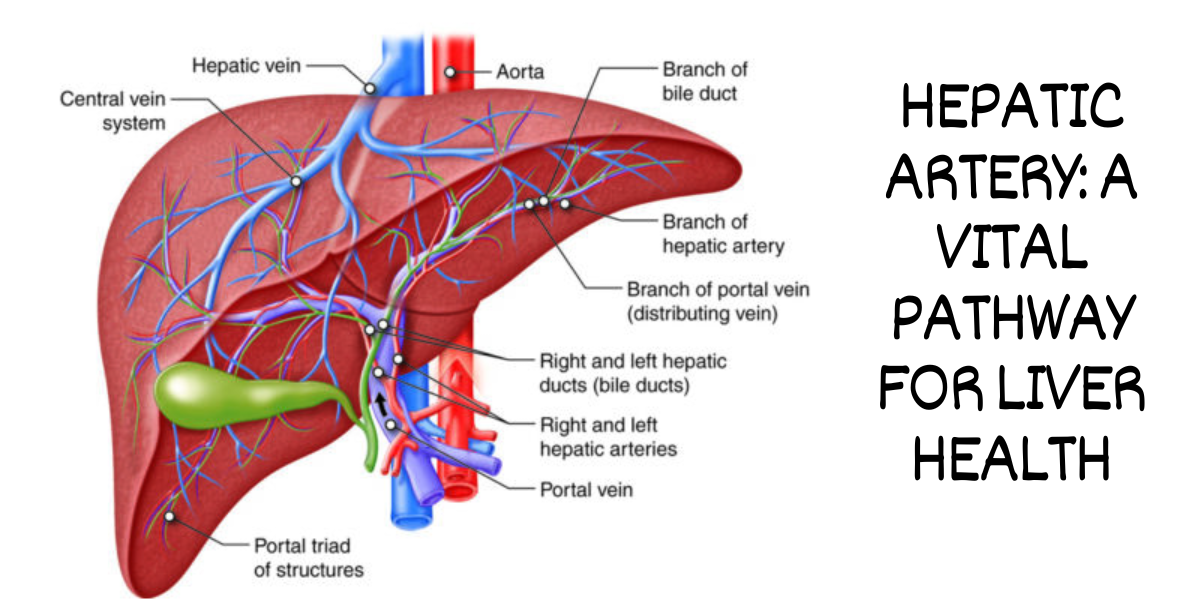
Anatomy of the Hepatic Artery
Branches of the Hepatic Artery
The hepatic artery branches into several smaller arteries that penetrate deeper into the liver tissue. These arteries ensure that every part of the liver receives the necessary oxygen and nutrients for optimal function.
Blood Supply to the Liver
The hepatic artery, along with the portal vein, provides blood supply to the liver. While the hepatic artery carries oxygenated blood, the portal vein delivers nutrient-rich blood from the digestive organs. This dual blood supply is vital for the liver’s multifaceted activities.
Importance of Oxygen-Rich Blood
Oxygen is a crucial element for cellular respiration and energy production. The liver’s cells require a constant supply of oxygen to carry out metabolic processes effectively, including the detoxification of harmful substances and the production of enzymes and proteins.
Interaction with the Portal Vein
The hepatic artery and the portal vein have a unique relationship within the liver. They form intricate networks that supply blood to different parts of the liver lobes. This collaboration ensures that both oxygen and nutrients are efficiently delivered to the liver’s diverse cells.
Common Issues with the Hepatic Artery
Hepatic Artery Thrombosis
Hepatic artery thrombosis occurs when a blood clot obstructs the artery’s flow. This can lead to tissue damage or even organ failure if not promptly addressed. Common causes include blood clotting disorders, trauma, or complications following liver transplantation.
Hepatic Artery Aneurysm
A hepatic artery aneurysm is a bulging and weakened area in the artery’s wall. While rare, it can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding if the aneurysm ruptures. Monitoring and treatment are crucial to prevent severe complications.
Diagnosis and Medical Imaging
Medical professionals utilize imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and angiograms to diagnose hepatic artery issues. These tools help visualize the artery’s structure, identify blockages, aneurysms, or other abnormalities, and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
Medications
Blood-thinning medications may be prescribed to prevent clot formation and promote healthy blood flow through the hepatic artery. Other medications may target underlying conditions contributing to artery issues.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. These can include procedures to remove blood clots, repair aneurysms, or even replace damaged portions of the artery with grafts.
Preventing Hepatic Artery Complications
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can contribute to overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Routine medical check-ups allow healthcare providers to monitor the liver’s health and detect any potential issues with the hepatic artery at an early stage.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research focuses on improving diagnostic tools, treatment methods, and preventive strategies related to hepatic artery complications. Advancements in medical technology continue to enhance patient outcomes and quality of life.
FAQs About the Hepatic Artery
- Is the hepatic artery the only blood supply to the liver?
- What symptoms might indicate a hepatic artery issue?
- Can lifestyle changes alone treat hepatic artery problems?
- How common are hepatic artery aneurysms?
- Are there alternative therapies for hepatic artery conditions?
Conclusion
The hepatic artery’s role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to the liver is pivotal for maintaining the organ’s multifunctional capabilities. Understanding its anatomy, importance, and potential complications empowers individuals to prioritize liver health. Regular medical check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt medical attention are key to ensuring the hepatic artery’s optimal function and preventing complications