Dengue Fever Symptoms
Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral infection, affects millions of people worldwide every year. The disease is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, where the Aedes mosquito, primarily the Aedes aegypti species, thrives. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of Dengue Fever Symptoms, from the common signs to the more severe manifestations of the disease.
1. Introduction
Definition of Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a viral infection caused by the Dengue virus, which belongs to the Flaviviridae family. There are four distinct serotypes of the Dengue virus, and infection with one serotype provides lifelong immunity against that specific serotype. However, subsequent infections with different serotypes can lead to more severe forms of the disease.

Prevalence and Global Impact
Dengue fever is a significant public health concern in many countries, especially in Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, the Caribbean, and parts of Central and South America. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 390 million Dengue infections occur annually, with severe cases resulting in around 20,000 deaths.
2. Understanding Dengue Virus
Transmission and Vector
Dengue virus is primarily transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female mosquitoes, mainly Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser extent, Aedes albopictus. These mosquitoes are known to be daytime biters and often breed in stagnant water, making urban areas particularly susceptible to Dengue outbreaks.
Different Strains of Dengue Virus
As mentioned earlier, there are four serotypes of the Dengue virus: DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4. While infection with one serotype confers immunity to that particular serotype, it also increases the risk of severe Dengue if the person is subsequently infected with a different serotype.
3. Incubation Period
Timeframe for Dengue Fever Symptoms to Appear
The incubation period for Dengue fever is typically 4 to 10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. During this period, the virus replicates in the body, and the infected person may remain asymptomatic.
4. Common Dengue Fever Symptoms
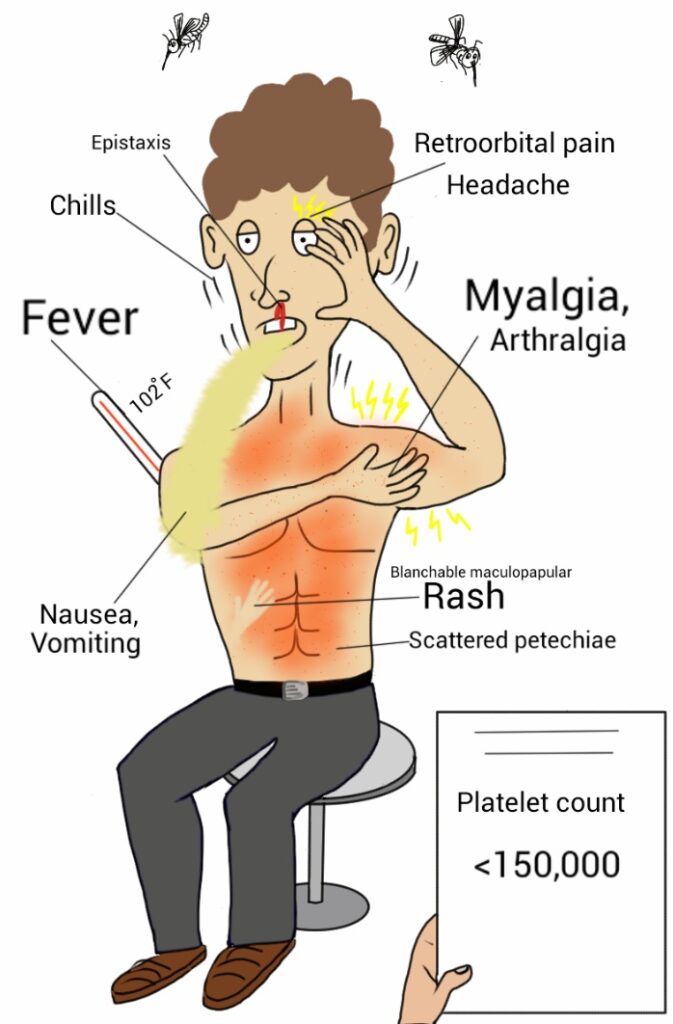
High Fever and Chills
One of the hallmark symptoms of Dengue fever is a sudden high fever, often reaching 104°F (40°C) or more. The fever is usually accompanied by chills and intense sweating.
Severe Headache and Eye Pain
Intense headaches, particularly in the forehead region, are common among Dengue patients. Eye pain, often described as retro-orbital pain, may also occur.
Muscle and Joint Pain
Dengue fever is sometimes referred to as “breakbone fever” due to the severe muscle and joint pain experienced by patients. The pain is typically localized in the lower back, limbs, and joints.
Nausea and Vomiting
Many Dengue patients experience nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite, which can contribute to dehydration.
Skin Rashes and Bruising
Skin rashes, similar to those in measles, may develop in the early stages of the disease. In some cases, Dengue can cause bleeding and bruising, leading to red spots on the skin.
5. Severe Dengue Symptoms
Warning Signs to Look Out For
In some cases, Dengue fever can progress to severe Dengue, which can be life-threatening. There are warning signs to watch for, including severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, bleeding gums, difficulty breathing, and fatigue.
Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a severe form of Dengue characterized by bleeding, plasma leakage, and organ failure. It is more likely to occur in individuals who have had a previous Dengue infection with a different serotype.
Dengue Shock Syndrome
Dengue shock syndrome is the most severe manifestation of Dengue fever, leading to a sudden drop in blood pressure, shock, and organ failure. Immediate medical attention is essential in such cases.
6. Diagnosing Dengue Fever
Physical Examination
Diagnosing Dengue fever often begins with a physical examination, during which the healthcare provider will look for characteristic symptoms and signs.
Blood Tests and Laboratory Analysis
Laboratory tests, including blood tests to detect the presence of Dengue virus or antibodies, are crucial in confirming the diagnosis.
7. Differential Diagnosis
Distinguishing Dengue Fever from Other Diseases
The symptoms of Dengue fever can overlap with other viral infections like Zika and Chikungunya, as well as illnesses such as malaria and typhoid fever. Differential diagnosis is essential to provide appropriate treatment.
8. Dengue Fever Treatment
Rest and Hydration
There is no specific antiviral treatment for Dengue fever. Supportive care, including rest and hydration, is essential to manage the symptoms.
Pain and Fever Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen can help reduce fever and alleviate pain. However, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
Hospitalization in Severe Cases
Patients with severe Dengue symptoms, such as bleeding, organ failure, or low platelet count, may require hospitalization for close monitoring and appropriate medical intervention.
9. Preventive Measures
Mosquito Control and Elimination
Preventing Dengue fever starts with controlling mosquito populations through measures such as removing stagnant water sources and using insecticides.
Protective Clothing and Repellents
Individuals in Dengue-prone areas should wear long-sleeved clothing and use mosquito repellents to reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
Vaccination Efforts
Vaccines for Dengue fever are under development, and some countries have approved the use of a Dengue vaccine. Vaccination efforts are crucial in controlling the spread of the disease.
10. Dengue Fever in Children and Pregnant Women
Unique Considerations and Risks
Children and pregnant women with Dengue fever require special attention, as the disease can have different impacts on these vulnerable populations.
11. The Impact of Climate Change on Dengue Fever
Altered Transmission Patterns
Climate change can influence the distribution and abundance of Aedes mosquitoes, potentially leading to shifts in Dengue transmission patterns.
12. Coping with Dengue Fever
Supportive Care and Mental Health
Recovering from Dengue fever can be physically and emotionally challenging. Supportive care and mental health support play a vital role in the recovery process.
13. FAQs about Dengue Fever Symptoms
What is the incubation period for Dengue Fever?
The incubation period for Dengue fever is typically 4 to 10 days.
Can Dengue Fever cause death?
While most Dengue cases are mild, severe Dengue can be life-threatening.
Is there a specific treatment for Dengue Fever?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for Dengue fever. Supportive care is the mainstay of treatment.
Are there any long-term effects of Dengue Fever?
In some cases, Dengue fever can lead to long-term fatigue and joint pain.
Can Dengue Fever be transmitted from person to person?
No, Dengue fever is primarily transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
In conclusion, Dengue fever is a significant global health concern, with its prevalence on the rise in many parts of the world. Understanding the symptoms and seeking early medical attention is crucial in managing the disease effectively. Preventive measures, such as controlling mosquito populations and ongoing efforts in vaccine development, are essential in reducing the impact of Dengue fever on communities worldwide.
If you have more questions or concerns about Dengue fever symptoms, check the FAQs above or consult a healthcare professional. Stay informed and vigilant, and together, we can combat Dengue and protect our communities from this debilitating disease